Kingston Smiler Selvaraj
Founder & CEO at PALC Networks ;⠀► Co-Chair at TIP (Telecom Infra Project) OOPT NOS Goldstone sub group 3 articles Following
Few months back I had written an article about the synergy between cloud providers and 5G providers wherein I had covered briefly about edge computing. Refer to the below link to read that article.
In this article I’m going to talk more details about the Edge Computing and Various Open Source alternatives of Edge Computing Platform. This is going to be a series of article and this article covers the introduction. Before getting into the edge computing platforms, let’s look into what is Edge Computing and various implementation of Edge Computing.
Edge Computing: Edge computing refers to running applications closer to the end user by deploying compute, storage, and network functions relatively close to end users and/or IoT endpoints. Edge computing provides a highly distributed computing environment that can be used to deploy applications and services as well as to store and process content in close proximity. Based on the type of edge device, the proximity and implementation of edge computing varies.
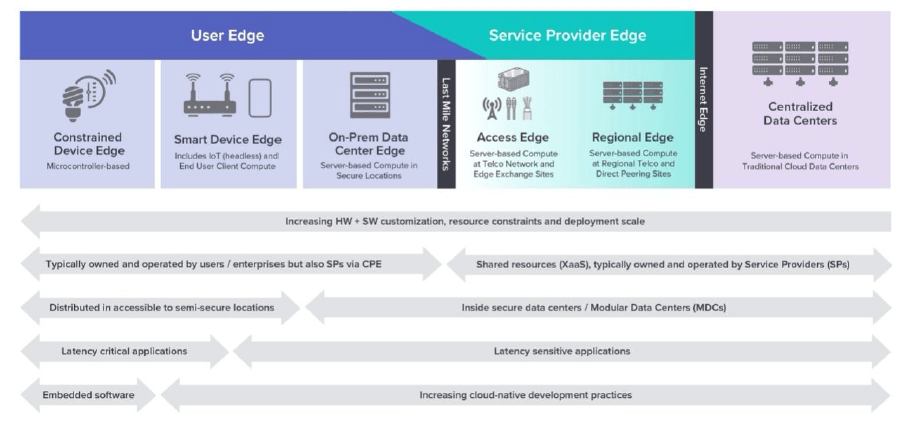
For example if the edge device is going to be a mobile phone, then the proximity of edge computing in 5G era is the network operator’s data centers at the edge of the 5G network using MEC implementation (service provide edge). On the other hand, if the edge device is going to be IoT nodes inside a manufacturing plant, then the proximity of edge computing is on-site within the production facility using Fog Computing implementation (user edge). The below diagram represents a high level view of user edge and the service provider edge.
So the implementation of Edge Computing differs based on the end nodes and been
defined with different implementations as
- Mobile Edge Computing / Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC)
- Fog Computing
- Cloudlet
Mobile Edge Computing / Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC)
MEC brings the computational and storage capacities to the edge of the network within the 5G Radio Access Network. The MEC nodes or servers are usually co-located with the Radio Network Controller or a macro base-station to reduce latency. MEC provides the ecosystem wherein the operators can open their Radio Access Network (RAN) edge to authorized third-parties, allowing them to flexibly and rapidly deploy innovative applications and services towards mobile subscribers, enterprises and vertical segments.
The MEC is an initiative from Industry Specification Group (ISG) within ETSI. The purpose is to create a standardized, open environment which will allow the efficient and seamless integration of applications from different vendors, service providers, and third- parties across multi-vendor Multi-access Edge Computing platforms. Full specification of MEC is available in https://www.etsi.org/committee/1425-mec
Some of the use cases of MEC are
- Video analytics
- OTT (Over the Top services)
- Location services
- Internet-of-Things (IoT)
- Augmented reality
- Optimized local content distribution and data caching
Fog Computing (FC)
Fog computing is a term created by Cisco that refers to extending cloud computing to the edge of an enterprise’s network. Fog computing is a decentralized computing infrastructure placed at any point between the end devices and the cloud. The nodes are heterogeneous in nature and thus can be based on different kinds of elements including but not limited to routers, switches, access points, IoT gateways as well as set-top boxes. Since cloud computing is not viable for many IoT applications, fog computing is often used to address the needs of IoT and Industrial IoT (IIoT). Fog computing reduces the bandwidth need and reduces the back-and-forth communication between sensors/IoT nodes and the cloud, which can affect the performance badly. Some of the use cases of FC are as follows
- Transportation / Logistics
- Utilities / Energy / Manufacturing
- Smart Cities / Smart Buildings
- Retail / Enterprise / Hospitality
- Service Providers / Data Centers
- Oil / Gas / Mining
- Healthcare
- Agriculture
- Government / Military
- Residential / Consumer
- Wearables / Ubiquitous Computing
Cloudlet
Cloudlets are similar to public cloud wherein the public cloud provider offers the end user with different offerings like compute, network and storage in the public cloud, however in cloudlets it will be offered in the edge closer to the user location. A cloudlet is basically a small-scale cloud however, unlike cloud computing that provides unlimited resources, the cloudlet can only provide limited resources. The services provided by Cloudlets are over a one-hop access with high bandwidth, thus offering low latency for applications. Cloudlet provides better security and privacy, since the users are directly connected to the cloudlet. Cloudlets are often compared are confused with Fog computing. Typically Fog computing are associated with IoT/ IIoT use cases whereas cloudlets are associated with use cases which requires the traditional cloud offerings in the Edge.
One of the important aspects of cloudlet is handoff across clouds / cloudlets. When a mobile device user moves away from the cloudlet he is currently using there is a need to offload the services on the first cloudlet to the second cloudlet maintaining end-to-end network quality. This resembles VM migration in cloud computing but differs considerably in a sense that the VM handoff happens in Wide Area Network (WAN).
Till now we have seen about the various implementation of edge computing. Now we are going to see the various platforms especially the open source platforms available in the
market to realize the edge platform.
The below are the list of platform available in the open source community for MEC segment
- Akraino Edge Stack (LF Edge)
- CORD (Linux Foundation)
- Airship (OpenStack Foundation)
- StarlingX (OpenStack Foundation)
The above list is not exhaustive.
There are many other projects for FOG / IoT use case like
- EdgeX Foundry (LF Edge)
- KubeEdge
- Eclipse IoFog (Eclipse)
- Baetyl (LF Edge)
- Eclipse Kura (Eclipse)
- Fledge (LF Edge)
- Edge Virtualization Engine (LF Edge)
- Home Edge etc. (LF Edge)
Below are some of the projects in cloudlet
- OpenStack++
- Elijah Cloudlet Project.
This is going to be a series of articles and in the next article, we are going to see the MEC
Edge stack in detail with Akraino Edge Stack and CORD.